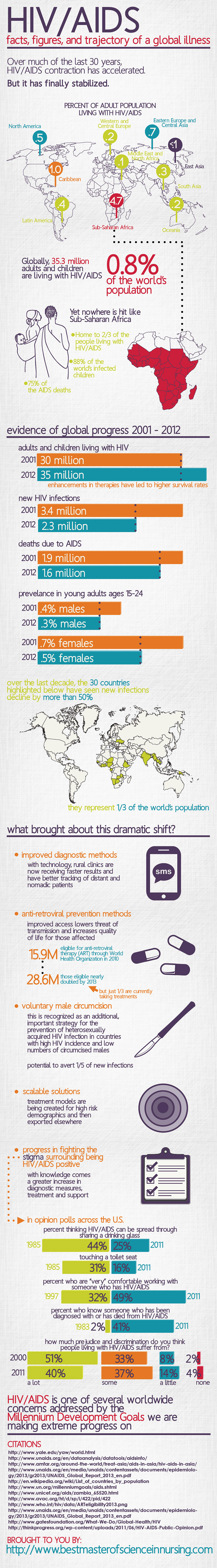
AIDS Today:
The facts, figures, and trajectory of a global illness.
Over much of the last 30 years AIDS contraction has accelerated.
But it’s finally stabilized.
Current hotspots:
North America:
1.1 million living with HIV/AIDS (.6% of adult population)
65,000 new infections yearly
20,000 AIDS related deaths yearly
South America:
2 million living with HIV/AIDS (1-2% of adult population)
210,000 new infections yearly
80,000 AIDS related deaths yearly
Europe:
.6 million living with HIV/Aids (.3% of adult population)
10,000 new infections yearly
3,000 AIDS related deaths yearly
Asia:
5 million living with HIV/AIDS (1.2% of adult population)
5 million new infections yearly
3.1 million AIDS related deaths yearly
Africa:
29.4 million living with HIV/AIDS (9% of adult population)
3.5 million new infections yearly
2.2 million AIDS related deaths yearly
Australia:
15,000 living with HIV/AIDS (.1% of adult population)
10,000 new infections yearly
7,000 AIDS related deaths per year.
Sub-Saharan Africa
Home to 2/3rd of people living with HIV
88% of the world’s infected children
And 75% of the world’s AIDS deaths.
Since the Millennium Development Goals (2000):
Goals:
2015: Have halted and reversed the spread of HIV/AIDS
2010: Universal access to treatment for HIV/AIDS (still in the works)
2001 vs. 2012
2001:
Adults and children living with HIV: 30 million
Newly infected with HIV: 3.4 million
Deaths due to AIDS: 1.9 million
Young people prevalence (15-24):
Male: .4%
Female:.7%
2012:
Adults and Children Living with HIV: 35.3 million
Newly infected with HIV: 2.3 million
Deaths due to AIDS: 1.6
Young people (15-24) prevalence:
Male: .3%
Female: .5%
Countries where adult HIV incidence has declined more than 50% since 2001: [4]
In ten years we’ve reduced the risk of HIV/AIDS by more than 50% for 1/3rd the planet.
1.) Belize 312,971
2.) Botswana 2,024,904
3.) Cambodia 15,135,000
4.) Cote d’Ivoire 23,202,000
5.) Djibouti 873,000
6.) Dominican Republic 9,445,281
7.) Eritrea 6,333,000
8.) Ethiopia 86,613,986
9.) Gabon 1,672,000
10.) Ghana 24,658,823
11.) India 1,238,990,000
12.) Jamaica 2,711,476
13.) Liberia 4,294,000
14.) Malawi 16,363,000
15.) Myanmar 53,259,000
16.) Namibia 2,113,077
17.) Nepal 26,494,504
18.) Niger 17,129,076
19.) Nigeria 173,615,000
20.) Papau New Guinea 7,059,653
21.) Sao Tome and Principe 187,356
22.) Senegal 13,567,338
23.) Thailand 65,926,261
24.) Togo 6,191,155
25.) Ukraine 45,447,010
26.) Zambia 13,092,666
Total Population: 1.869 Billion
The third of the planet previously hit hardest by the virus.
What Enabled Such a Drastic Shift?
1.) Improved Diagnostic Methods
SMS Diagnostic Services
Old way: lengthy delay from HIV test laboratory to rural health clinics. Plus, lengthy delay for those in the country, often walking to get into rural health clinics.
Also: no way to contact nomadic peoples who are tested.
Today: SMS (text) results
Enables: better tracking of millions of patents.
quicker results, for quicker treatment (ex. babies who received the illness at birth).
2.) Anti-Retroviral Prevention Methods
Improved access to drugs that reduce viral load.[8]
–> Lowering threat of passing on aids
–> Increasing quality of life for HIV/AIDS sufferer.
Access to antiretroviral therapy in low/middle income countries has doubled in the last 3 years. [9]
2010:
On Anti-retroviral therapy (ART): 9 million
Eligible for ART: 15.9 million
2013:
On ART: 10 million
Eligible for ART: 28.6 million
3.) Voluntary Male Circumcision
Circumcising 80% of all uncircumcised males in high AIDS prevalence countries.
By 2015.
Would avert 1/5 of new HIV infections WORLDWIDE by 2025.
4.) Scalable solutions
Create scalable treatment models
Try them in high risk demographics:
India, China, Myanmar, and Botswana
Then export them elsewhere.
5.) Fighting the stigma surrounding HIV/AIDS positive people. [11]
By fighting the stigma and fear surrounding HIV/AIDS, the urge to seek treatment, diagnostic measures, and support is greatly increased.
American Opinion Polls:
% mistakenly thinking HIV can be spread through:
Sharing a drinking glass:
1985: 44%
2011: 25%
Touching a toilet seat:
1985:31%
2011:16%
% who know someone who has been diagnosed with, has, or has died of HIV/AIDS:
1983: 2%
2011: 41%
% “very” comfortable working with someone who has HIV/AIDS:
1997: 32%
2011: 49%
How much prejudice and discrimination do you think people living with HIV/AIDS in our country suffer from?:
2000:
A lot–51%;Some 33%;Only a little 8%; None at all 2%
2004::
A lot 45%; Some 38%; Only a little 9%; None at all 2%;
2006:
A lot 45%; Some 36%; Only a little 11%; None at all 3%;
2011:
A lot 40%; Some 37%; Only a little 14%; None at all 4%;
HIV is one of several worldwide concerns addressed by the Millennium Development Goals we are making extreme progress on.
Citations: